Nerve Compression
Contents
What is Nerve Compression?
It is a group of musculoskeletal problems that occur due to the compression of nerves in the grooves they pass through, and progresses with pain and numbness. It is also called Entrapment Neuropathies. In advanced cases, weakness and loss of strength may occur in the muscles they work.
What Causes Nerve Compression?
Muscles are connected to each other by membranes called fascia. These connections are important in the formation of some automatic movement patterns such as working with the hands and walking. These automatic patterns save the brain from thinking about every movement, but a problem that occurs in a muscle within the movement pattern spreads to other muscles. The ligaments that the nerves pass under or through are also part of the fascia. Any problem that may occur in the fascia chain to which these ligaments are attached also affects the ligament. If the process continues and becomes chronic, it puts pressure on the nerve passing under or through it, thus entrapment neuropathies occur.
Which Nerves Are Compressed?
Many nerves in the arms and legs can be compressed. However, the most common Entrapment Neuropathies are as follows.
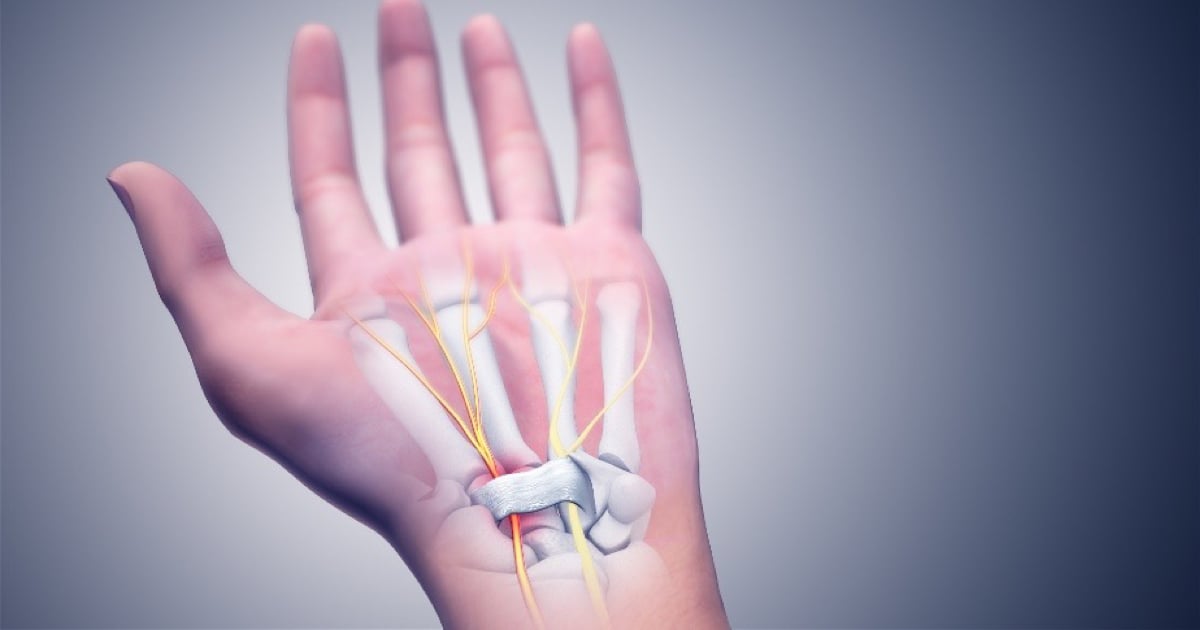
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
There is a tunnel formed by the carpal ligaments on the side of the wrist that bends inward. The median nerve that goes to the first 3 fingers of the hand passes through here. The compression of the median nerve due to the narrowing of the carpal tunnel causes numbness in the first 3 fingers, and if it progresses, muscle atrophy and weakness.
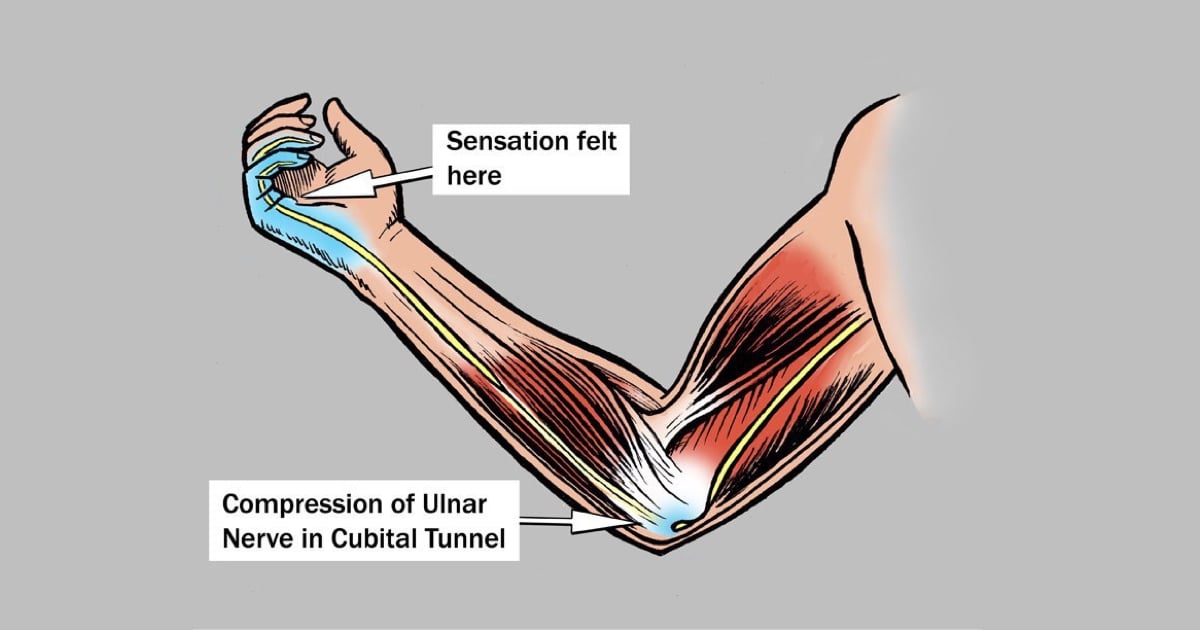
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
The groove formed by the ligaments on the inside of the elbow and through which the cubital nerve passes, which goes to the 4th and 5th fingers of the hand, is called the cubital tunnel. The narrowing of this channel causes pressure on the ulnar nerve, resulting in numbness in the 4th and 5th fingers, and in advanced cases, weakness and muscle atrophy.
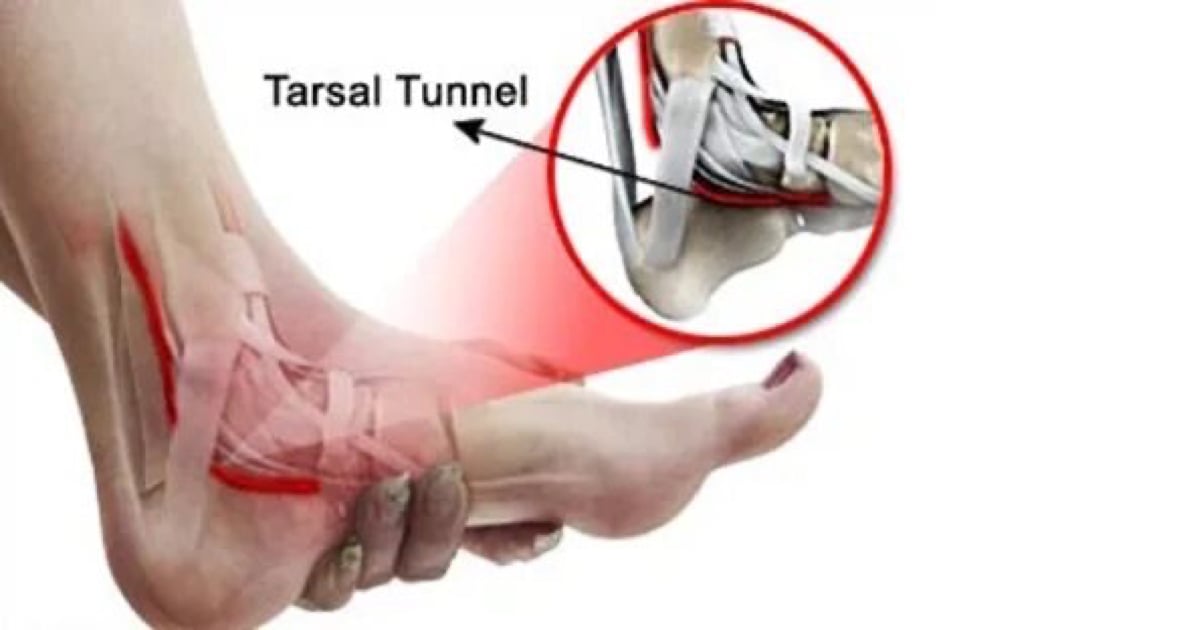
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
The groove formed by the ligaments on the inner side of the ankle is called the tarsal tunnel. As a result of the narrowing of this channel, the compression of the tibial nerve passing through it causes pain and numbness in the sole of the foot.
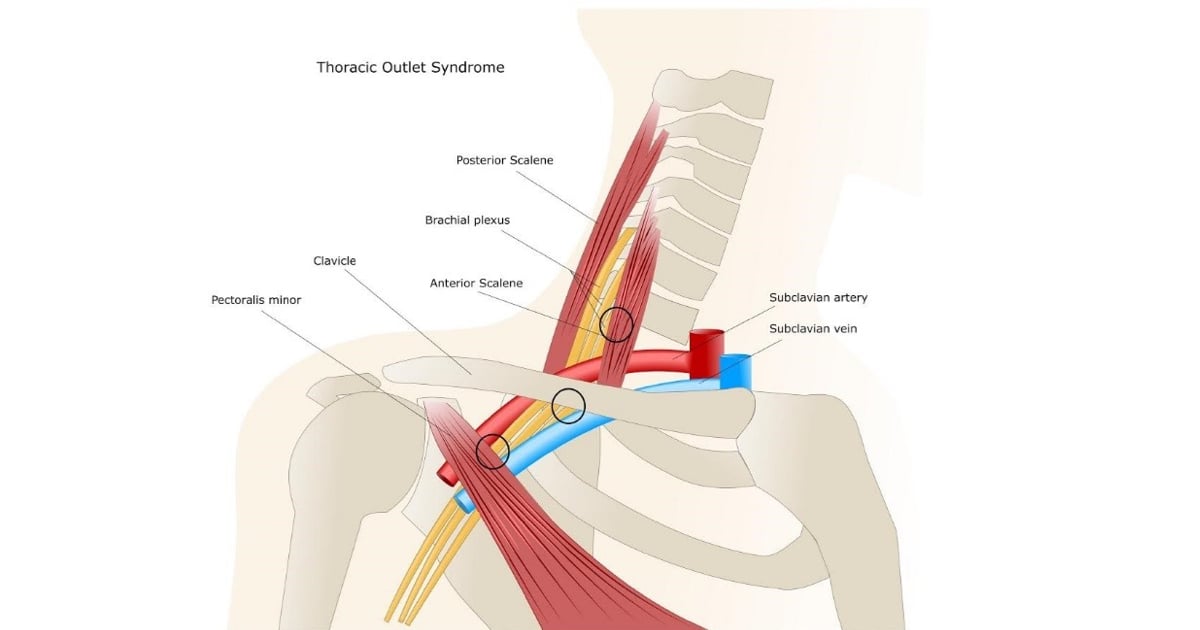
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
A clinical picture that occurs when the vascular nerve bundle going to the arm is compressed at the thoracic outlet, the rib cage outlet. It causes pain and numbness in the arm and sometimes swelling. The most important cause is tension in the scalene and pectoralis minor muscles.
How is it Treated?
The general classical approach is to first give painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs and splints. If it does not go away, cortisone injections and physical therapy are recommended. If it does not go away with these, surgical release is recommended.
The channels where nerve compressions are located are part of the fascia chains. Loosening the fascia chains to which the compressed nerve is attached and the trigger points located here with the neural therapy technique gives radical and permanent results.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do you have any other questions?
We created this section to help you quickly find the information you need. Finding answers to your questions is easy. If you need more details, you can use the contact form.